This is the lecture note of CS61A - Lecture 3.
Print and None
The speacial value None represents nothing in Python.
A function that does not explicitly return a value will return None. None is not displayed by the interpreter as the value of an expression.
1 | 'Go Bears!' |
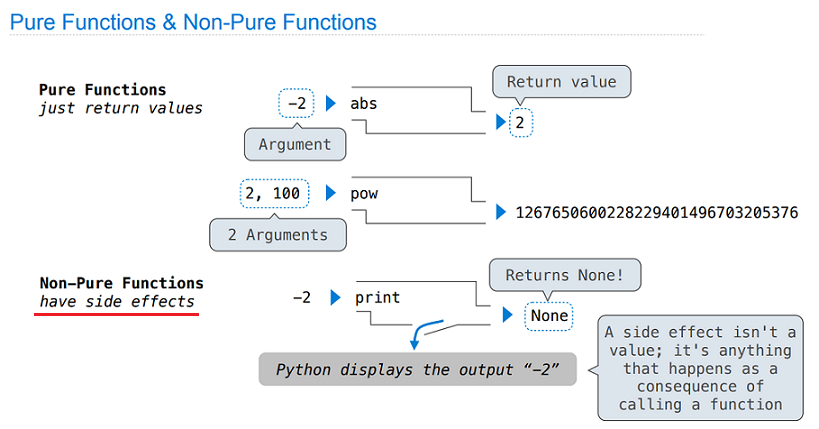
print is a non-pure function, it can generate side effects. The value that print returns is always None.
Pure functions are essential for writing concurrent programs, in which multiple call expressions may be evaluated simultaneously.
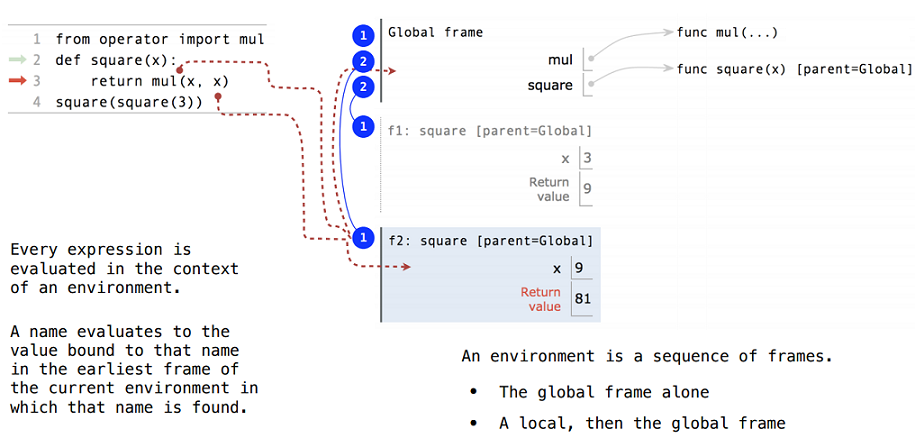
Multiple Environments
When Python executes a program, different expressions can be evaluated in different environments.
Miscellaneous Python Features
- division
1 | # Division |
- multiple return values
1 | # Multiple return values |
- docstring, doctest & default arguments
1 | # Docstrings, doctests, and default arguments |
- useful command line:
1 | # interactive with Python file |
Conditional Statements
A statement is executed by the interpreter to perform an action.
Conditional statements let programs execute different lines of code depending on certain conditions.
- False values in Python: False, 0, ' ', [ ], None, { }
- True values in Python: anything else
1 | # Conditional expressions |
A conditional expression also has the following form:
1 | <consequent> if <predicate> else <alternative> |
Logic Operators
To evaluate the expression <left> and <right>:
- Evaluate the subexpression
<left>. - If the result is a false value v, then the expression evaluates to v.
- Otherwise, the expression evaluates to the value of the subexpression
<right>.
1 | True and 4 |
To evaluate the expression <left> or <right>:
- Evaluate the subexpression
<left>. - If the result is a true value v, then the expression evaluates to v.
- Otherwise, the expression evaluates to the value of the subexpression
<right>.
1 | 4 or True |
1 | # Examples of short- circuiting behavior |
Iteration
Iteration means repeating things.
1 | # Summation via while iteration |
- Example: Prime Factorization
1 | def prime_factors(n): |